2013 Drought Outlook
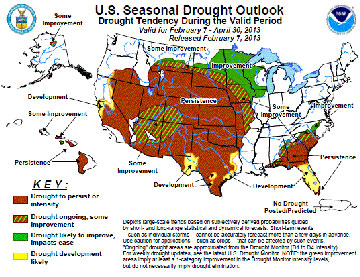 The National Weather Service Climate Prediction Center’s 2013 U.S. Seasonal Drought Outlook predicts a persistence or intensification of the drought continuing across much of the Great Plains and Intermountain West, with some improvement in the Northern Plains as we head into early spring. In addition, the U.S. Drought Monitor continues to show little improvement with approximately 77% of western states, 95% of High Plains states, and nearly 69% of southern states still in varying degrees of drought conditions. For many in these areas, this could be the second, or even worse, third or more years of on-going drought. It is these consecutive years of ongoing drought where management decisions are most vital. To combat drought, a drought plan is a necessity.
The National Weather Service Climate Prediction Center’s 2013 U.S. Seasonal Drought Outlook predicts a persistence or intensification of the drought continuing across much of the Great Plains and Intermountain West, with some improvement in the Northern Plains as we head into early spring. In addition, the U.S. Drought Monitor continues to show little improvement with approximately 77% of western states, 95% of High Plains states, and nearly 69% of southern states still in varying degrees of drought conditions. For many in these areas, this could be the second, or even worse, third or more years of on-going drought. It is these consecutive years of ongoing drought where management decisions are most vital. To combat drought, a drought plan is a necessity.Key Components of Drought Planning
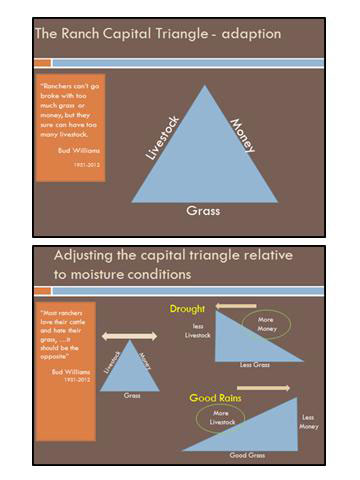
In ranching we manage three key resources – grass (which represents the land), livestock, and money. “Ranchers can’t go broke with too much grass or money, but they sure can have too many livestock,” Bud Williams many times would say. “Most ranchers love their cattle and hate their grass?it should be the opposite.”
In times of good moisture, it is possible to run more livestock. But in dry times, destocking to some degree will mean more capital available to reinvest into livestock when conditions do improve. Ideally, ranchers should seek to leave their lands coming out of a drought in comparable condition to when the drought began. Planning and preparation can make this a possibility.
This preparation process includes several key components:
– Good grazing management
– A grazing budget
– Tracking and recording of precipitation on the ranch
– Determination of critical rainfall dates
When implemented correctly these components will work together to help minimize risk, and when the time comes for destocking decisions, land stewards are in a better position to make them.
Grazing Management
Key considerations for making grazing management decisions during drought will include length of rest period for forage plants, season of grazing use, year-end residual, and amount of precipitation. Tools such as a grazing index and a forage resource budget can assist in these decisions.
A grazing budget accounts for all forage resources necessary to sustain a livestock through a given period of time. This can be done through use of tools such as a grazing calculator or budget spreadsheet. With this working inventory in hand, a determination of pasture carrying capacity in years with near-average precipitation can be calculated.
Combined with observations of current rangeland conditions and residual forage available, this information will be vital when it is time to make decisions, such as destocking due to inadequate forage availability.
New Tool – Grazing Budget Snapshot
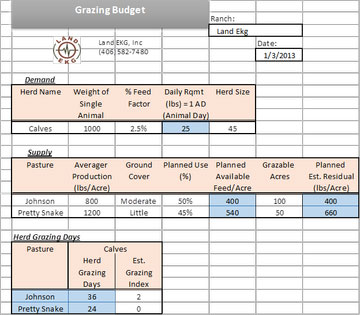 A grazing budget spreadsheet is one of the fun projects we have been working on here in the office to help make drought and grazing planning easier for YOU! When it comes to planning for an upcoming grazing season, you should have an idea of how much grass you want to be taken and -more importantly; leftover – relative to the pasture’s production and ground cover. From that, you should be able to determine how many grazing days any herd should have in a given pasture relative to your planned available feed.
A grazing budget spreadsheet is one of the fun projects we have been working on here in the office to help make drought and grazing planning easier for YOU! When it comes to planning for an upcoming grazing season, you should have an idea of how much grass you want to be taken and -more importantly; leftover – relative to the pasture’s production and ground cover. From that, you should be able to determine how many grazing days any herd should have in a given pasture relative to your planned available feed.
To do this we have created a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet entitled “Grazing Budget Snapshot,” (see left) which is a condensed version of our “Grazing Budget Template.” (click here to download Excel template). The “Grazing Budget Snapshot” has been designed to ultimately provide you with the number of grazing days that a pasture will have for a given number of animals. Relative to the grazing days calculated by the worksheet, a grazing plan can then be developed.
Click to download the Grazing Budget Snapshot Excel spreadsheet template.
The spreadsheet is simple to use and works like this:
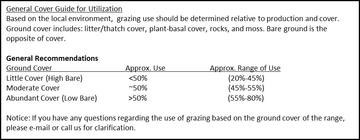 The white cells are to be filled in by you (horizontally). First, fill in the white cells in the Demand section, followed by the white cells in the Supply section. You will notice that as you fill in enough of the white cells, the blue cells begin to automatically calculate the values for you. The only cells that you can enter data into are the white cells within the Supply, Demand, Herd Grazing Days, Notes, Ranch, and Date categories. All other cells have been locked so that equations, formatting, and structure of the worksheet cannot be modified.
The white cells are to be filled in by you (horizontally). First, fill in the white cells in the Demand section, followed by the white cells in the Supply section. You will notice that as you fill in enough of the white cells, the blue cells begin to automatically calculate the values for you. The only cells that you can enter data into are the white cells within the Supply, Demand, Herd Grazing Days, Notes, Ranch, and Date categories. All other cells have been locked so that equations, formatting, and structure of the worksheet cannot be modified.Once the necessary cells from the Supply and Demand sections have been filled in, the Herd Grazing Days will have calculated values according to each Herd Name and Pasture. We gave you the option of filling in the Estimated Grazing Index for each herd and pasture. For more information on using the grazing index see the following link: Land EKG™ E-Newsletter – September 2009
Feel free to play with the Excel spreadsheet to get a feel for how it works. It has been designed to be simple and user-friendly. The full “Grazing Budget Template”, which allows you to enter data for up to four total herds and 29 pastures with individual notes for each, can be acquired by calling our office (307-366-2445) or contact us by email. If you have any questions about the “Snapshot Grazing Budget” or anything else, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Google Earth for Ranch Mapping
 Another tool that will prove useful to ranchers monitoring land conditions as part of their drought planning is Google Earth (GE). GE’s timeslider feature allows for users to access historical imagery snapshots of landscapes over time. The example to the left shows how GE can be used to track and record vegetative cover over time at a single location relative to climatic conditions, such as drought.
Another tool that will prove useful to ranchers monitoring land conditions as part of their drought planning is Google Earth (GE). GE’s timeslider feature allows for users to access historical imagery snapshots of landscapes over time. The example to the left shows how GE can be used to track and record vegetative cover over time at a single location relative to climatic conditions, such as drought.GE’s affordability — free — and relative ease of use truly makes it a management game-changer for ranchers. In less than a few hours of training, anyone can learn to map. To help ranchers learn to use this game changing technology, we are offering a 3-part webinar series titled “Intro to Google Earth Ranch Mapping – 2013” that will leave users confident and excited about the possibilities and benefits Google Earth makes available to land managers. Through this webinar series participants can expect to learn effective use of GE to:
– Map basic ranch borders, pasture fence, trails, ponds, and water points
– Develop and archive annual grazing plans
– Map weeds and management strategies
– Verify the most effective practices
– Track and develop your land monitoring program
– Plan future land and pasture improvements (i.e. water lines, fencing, vegetation control, and habitat improvement practices)
– Print maps and specific management plans for employees, agencies, etc.
– Easily share map files back and forth
The 3-part series will be held over a course of three weeks on February 28th, March 7th and 14th. Each will consist of an hour in length. In addition, for those ranchers that are interested but may not be able to attend the live webinars, sessions will be recorded and access given to participants. The Land EKG Team will be available for technical support and follow up questions after the event. Cost to participate for the webinar series (3 weeks, 1hr/week) and follow up technical support are $99 (US funds).
If you have any suggestions for future issues, have feedback, or want more information please contact us at:
(307) 366-2445 or contact us by email.
